All players who care about high performance, fluency of play, and low latency always look for ways to improve their PC. Before you buy a new processor, graphics card, or RAM setup, it’s worth knowing what gives you the highest speed.
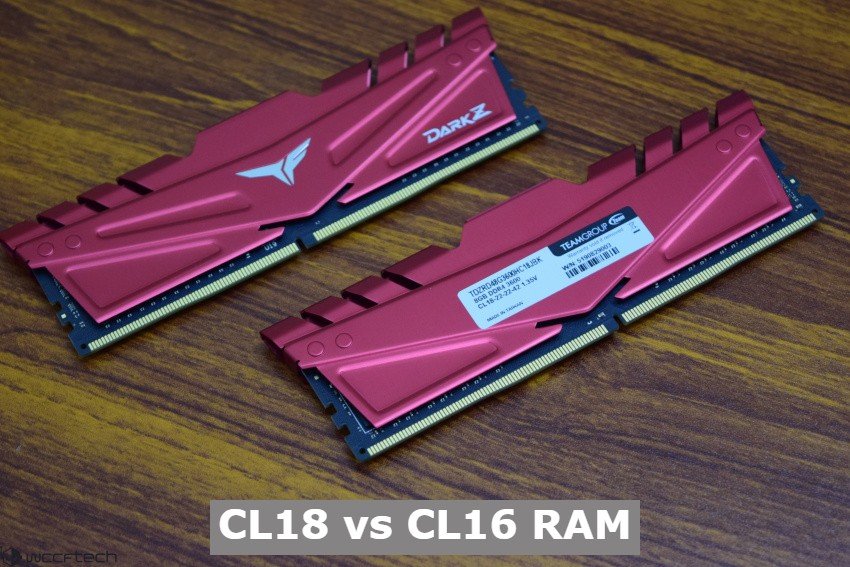
CL16 is superior to CL18 because it has a lower CAS latency, which means that it takes fewer cycles to process and make the data available to your CPU. CL16 RAM will provide players with a faster response time than CL18 RAM with the same memory speed because it processes data in 16 cycles instead of 18 cycles like RAM CL18 does.
For many people with inexperienced eyes, the difference is negligible. The main factor determining how remarkable the difference is whether or not you have a Ryzen CPU. So how can you know which one you need?
In this article, I will review the CL in depth, as well as the differences between the latency of the CAS and the speed of the RAM and how they affect the players who use various CPU marks. Let’s start.
¿What does CL mean?
CL stands for Column Access Strobe Latency ( column access latency ) and refers to how fast RAM can process and prepare data in response to processor orders. Lower CAS latency means faster overall performance.
If you compare a memoryRAM CL16 of 3200 MHz with a RAM CL18 of 3600 MHz, You will notice that, despite the higher speed of CL18 memory, CL16 has better performance, and that it improves as memory speed increases. This is because the speed of memory and the latency CAS are not the same.
CAS Latency
The number of clock cycles it takes for RAM to process a processor order is known as the CAS latency. Lower CAS latency means higher performance, regardless of memory speed ( assuming that CL16 and CL18 are not separated by more than 1,000 Hz ).
Players who want to reduce the latency of their RAM should opt for a CL16 instead of a CL18, since it will surpass the latter in all aspects that matter to the players.
CAS Latency 3200 MHz vs. 3600 MHz
If you compare the 3200 MHz RAM with the 3600 MHz RAM, you will see that the mean CL range of the 3200 MHz RAM is 14-16, while the CL range of 3600 MHz RAM is 15-19. The first has a higher rank, but the rank of the second has a lower minimum. This means that, despite its higher memory speed, a 3200 MHz CL14 RAM will outperform a 3600 MHz CL18 RAM.
The same is true when comparing a 3200 MHz CL16 RAM with a 3600 MHz CL18, but the difference is not so noticeable. As the average player will hardly notice the difference ( approximately 5% ), Most people ignore CL and opt for faster memory speeds without realizing what is being lost.
If you want to get the most out of your computer, you will want the least CAS latency possible. You can know the CAS latency of your RAM by consulting the manufacturer’s website or looking at your RAM. In memory, you will see a series of three or four numbers, the first of which is the CAS latency.
RAM Latency
The latency of RAM memory is different from CAS latency, but it has less impact on RAM performance than might be thought. The time it takes for memory to complete a clock cycle per second is called RAM latency.
The latency of the RAM is measured in nanoseconds and is calculated by dividing the speed of memory by the CAS latency. Let’s compare the latency of RAM memory from a CL16 to 3200 MHz and from a CL18 to 3600 MHz.
The latency of the 3200 MHz RAM CL16 is 10 nanoseconds, which means that each clock cycle takes 10 nanoseconds to complete. To receive and process each data stream, the RAM must complete 16 clock cycles with a CL16. Simply put, it takes 160 nanoseconds for a command to go from input to output.
The 3600 MHz RAM CL18 has a latency of 10 nanoseconds, but it takes 18 clock cycles to go from the entrance to the exit with a CL18. This results in a total process time of 180 nanoseconds, representing an increase of 12% compared to the 3200 MHz CL16.
In most cases, a CL16 can outperform a CL18 despite having a higher memory speed.
RAM Speed vs. RAM Latency
¿What is the difference between the speed and latency of a RAM?
The megahertz, or “MHz”, is the unit of measurement for the speed of the RAM. It is a measure of the clock speed of a RAM, which determines how many times you can access RAM to your memory per second.
This means that a 3200 MHz RAM can access memory 3200 times per second, while a 3600 MHz RAM can access memory 3600 times per second. The more memory speed contributes to RAM performance, the better.
As already stated, the latency of RAM is the time it takes for memory to complete a clock cycle, which is determined by the speed of RAM. Higher speed of RAM memory results in lower latency of RAM, which translates into higher performance.
How CAS Latency Plays in RAM Speed and Latency
Now that you know what the three main components influence the performance of RAM, you can learn how they interact.
For starters, faster RAM means lower RAM latency, which means your RAM can access memory more times per second with less time between cycles.
In this case different specifications of CAS latency are used. Your RAM can complete the command in fewer cycles with a lower CL rating than with a higher CL rating. Let’s see it again, this time using 3200 MHz and 3600 MHz RAM as a reference.
CL16 vs. CL18 3200 MHz
A CL16 3200 MHz will work much faster than a CL18 3200 MHz at this memory speed. CL16 and CL18 have a similar latency, with CL18 being slightly slower. RAM can access your memory 3200 times per second. As a result, you can process data faster with a CL16 RAM, since it takes two cycles less to complete the task than a CL18 RAM, and there is less latency in the RAM.
CL16 vs. CL18 3600 MHz
The same is true in this case. CL16 3600 MHz has a lower mean nanometer RAM latency than CL18 3600 MHz. This means that although both can access memory at 3,600 times per second, CL18 has a slightly longer access cycle delay than CL16.
With a slightly larger margin, the difference between the two would be less noticeable than if compared to 3200 MHz.
How different CPUs affect RAM performance
AMD CPUs
Ryzen CPUs are designed with an infinite fabric core system, also known as AMD’s IF, the kings of proprietary computing technology. The IF system has its own clock time characteristics, known as FCLK, and is limited to clock speeds of about 2000 MHz.
So if you have a Ryzen CPU, you can largely ignore the clock speed and focus on a lower CL. By reducing the number of cycles required to process a command, you can take full advantage of Ryzen’s tight clock cycles.
Intel CPUs
If you use an Intel processor, you will want to do the opposite. Since Intel processors don’t have such tight clock cycles, a faster memory speed will help you get the most out of your processor.
You can overclock the CL from 18 to 16 with higher memory speed and CL in a Ryzen with CL18, which will give you faster performance than a Ryzen with CL18.
Conclusion
In almost every respect, a CL16 will outperform a CL18 for most purposes. Regardless of the actual memory speed, fewer cycles are needed to process a command. The only case a CL18 could outperform a CL16 is if you use an Intel processor, and even then, you will have to overclock the RAM to make it work as well as the CL16.